U/S SCAN ABDOMEN
Know More About This Test
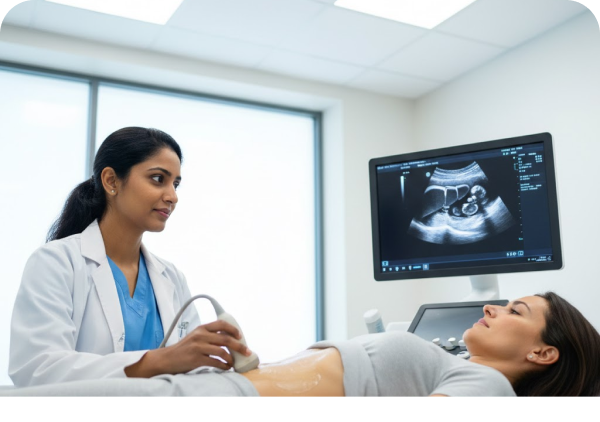
The Ultrasound (U/S) Scan Abdomen is a non-invasive imaging test used to assess the abdominal organs. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of structures such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, major blood vessels, and surrounding soft tissues. It helps detect abnormalities like inflammation, stones, cysts, masses, or fluid collection. As this test uses no radiation, it is safe for all age groups, including pregnant women.
Why should I take this Test?
To evaluate abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, or unexplained discomfort.
To examine the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and kidneys for structural abnormalities.
To detect gallstones, kidney stones, liver disease, pancreatitis, or abdominal masses.
To assess for fluid in the abdomen (ascites) or enlargement of abdominal organs.
To investigate suspected infections, obstruction, or vascular abnormalities in the abdomen.
Understanding U/S SCAN ABDOMEN
The U/S Scan Abdomen provides detailed visualization of the upper and lower abdominal organs using sound waves. It helps assess organ size, shape, texture, and any abnormal findings such as stones, cysts, or masses. Doppler ultrasound may be used when needed to evaluate blood flow in abdominal vessels.
Findings may include areas of increased or decreased echogenicity, fluid pockets, organ enlargement, or structural irregularities. Interpretation should always be done by a qualified doctor who will correlate results with symptoms for proper diagnosis and further treatment planning.
What Does the U/S SCAN ABDOMEN Measure?
This scan evaluates:
Size, shape, and texture of abdominal organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys).
Presence of gallstones, kidney stones, cysts, tumors, or inflammation.
Blood flow in major abdominal vessels using Doppler (if advised).
Fluid accumulation (ascites) or abnormalities in surrounding soft tissues.
Obstruction in the bile ducts or urinary tract.
Serial scans may be used to monitor disease progression, treatment response, or post-operative changes.
What to Expect During the Procedure
An abdominal ultrasound is simple and typically takes 15–30 minutes. Here’s what happens:
Positioning: You’ll lie on your back or side on an examination table.
Application of Gel: A water-based gel is applied to your skin to ensure smooth transmission of sound waves.
Scanning: A handheld device called a transducer is moved across your abdomen. It emits sound waves and captures their echoes to generate images.
Real-Time Observation: The technician or radiologist views these images on a monitor to assess organ health and function.
After the procedure, you can resume normal activities immediately unless instructed otherwise.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits:
Non-invasive and painless.
Radiation-free, making it safe for all age groups, including pregnant women.
Provides real-time imaging.
Limitations:
It may not detect small abnormalities in deep structures.
Gas in the intestines can obscure images.
Not suitable for evaluating bones or lungs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is an abdominal ultrasound a safe procedure?
Yes. This scan uses harmless sound waves and does not expose you to radiation, making it safe for adults, children, and pregnant individuals.
2. How long does an abdominal ultrasound usually take?
Most scans are completed within 15–30 minutes. The duration may vary slightly based on the organs being examined.
3. Will I experience any discomfort during the test?
No significant discomfort is expected. You may feel gentle pressure from the probe and cool gel on the skin, but the procedure is painless.
4. Do I need a referral from a doctor before scheduling the scan?
A referral is generally recommended so that the scan is performed for the right clinical reason, but some centers may allow booking without one.
5. How often should I undergo an abdominal ultrasound?
There is no fixed frequency. The scan is done based on medical need—either for routine monitoring of known conditions or when new symptoms appear.
6. Which abdominal organs are assessed during this scan?
The test typically evaluates the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and major abdominal blood vessels. In some cases, the bladder or other structures may also be reviewed.
7. What symptoms or conditions may require this test?
It is commonly advised for abdominal pain, bloating, jaundice, vomiting, suspected stones, or abnormal liver or kidney test results.
8. Is this scan safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Yes. Ultrasound is the preferred imaging method during pregnancy because it uses no radiation and has no known risks for mother or baby.
9. How does the ultrasound machine create images?
The probe sends out sound waves that bounce off internal organs. These echoes are converted into real-time images displayed on the screen.
10. Will I be exposed to radiation during this scan?
Not at all. Ultrasound relies only on sound waves, unlike X-ray or CT scans.
11. Can I bring someone with me to the appointment?
Yes, most facilities allow a companion for comfort and support, except in restricted clinical areas.
12. Do I need sedation for the abdominal ultrasound?
No sedation is required. You will be awake, comfortable, and able to follow simple instructions during the scan.
13. Can I continue taking my regular medications before the test?
Yes, you may take your usual medications unless your doctor provides specific instructions, such as fasting for certain abdominal evaluations.
14. I am claustrophobic—will that affect the test?
Not at all. The procedure is done in an open room without any enclosed spaces.